0.Github
CrystalChanB31/clip_on_plantvillage: CLIP模型在PlantVillage植物病害识别任务中的应用探究
1.环境准备
1.1 数据集
显卡:Nvidia Geforce RTX5090 @ 32GB * 1
1.2 软件环境配置
Linux:Ubuntu 24.04LTS(WSL2)
Anaconda:最新版本
CUDA:13.0
Python version info: 3.10.19 (main, Oct 21 2025, 16:43:05) [GCC 11.2.0]
PyTorch version info: 2.10.0.dev20251026+cu130
1.3 requirements.txt
torch>=1.12.0
torchvision>=0.13.0
scikit-learn>=1.0.0
tqdm>=4.0.0
pillow>=8.0.0
numpy>=1.19.0
# OpenAI CLIP: install from the official GitHub repo
# This installs the `clip` package used in the code (ViT-B/32, etc.).
# If you prefer a released wheel or your environment already contains CLIP, you can omit the line below.
git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git@main#egg=clip2.数据处理
2.1 先进行数据集的划分(测试集,训练集和验证集)
数据分类方法:
下载的数据集中分为 color , grayscale , segmented 三个文件夹,这里以 color 文件夹为例:
- 训练集比率:70%
- 验证集比率:20%
- 测试集比率:10%
2.2 创建数据划分方法文件split_data.py
# Plantvillage/split_data.py
import os, shutil, random, sys
from pathlib import Path
# ===== 配置区 =====
SRC_DIR = Path("./dataset/color") # 你的源数据:color 文件夹路径
DEST_DIR = Path("./Plantvillage") # 目标根目录:会生成 train/val/test
TRAIN_RATIO, VAL_RATIO, TEST_RATIO = 0.7, 0.2, 0.1
SEED = 42
CLEAR_DEST = False # 若你多次尝试,想先清空再重新拷贝,改为 True(小心!会删除目标目录)
# ===== 工具函数 =====
IMG_EXTS = {".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png", ".bmp", ".tif", ".tiff"}
def list_images(d: Path):
return [p for p in d.iterdir() if p.is_file() and p.suffix.lower() in IMG_EXTS]
def ensure_dirs(*dirs):
for d in dirs:
d.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
def copy_many(paths, target_dir: Path):
ensure_dirs(target_dir)
for p in paths:
shutil.copy2(p, target_dir / p.name)
def split_indices(n, tr=TRAIN_RATIO, vr=VAL_RATIO, te=TEST_RATIO):
"""对长度为 n 的数组索引,返回 (train_idx, val_idx, test_idx)"""
idx = list(range(n))
random.shuffle(idx)
if n == 0:
return [], [], []
if n == 1:
return idx, [], [] # 1张:全放train
if n == 2:
return idx[:1], idx[1:], [] # 2张:1/1/0
if n == 3:
return idx[:2], idx[2:], [] # 3张:2/1/0
if n == 4:
return idx[:3], idx[3:], [] # 4张:3/1/0
# n >= 5 用比例
n_train = max(1, int(round(tr * n)))
n_val = max(1, int(round(vr * n)))
# 确保不超
if n_train + n_val >= n:
n_val = max(1, n - n_train - 1)
n_test = n - n_train - n_val
if n_test < 0:
n_test = 0
# 再次纠偏
n_val = min(n_val, n - n_train)
tr_idx = idx[:n_train]
va_idx = idx[n_train:n_train+n_val]
te_idx = idx[n_train+n_val:]
return tr_idx, va_idx, te_idx
def main():
random.seed(SEED)
if not SRC_DIR.exists():
print(f"[ERR] 源目录不存在:{SRC_DIR.resolve()}")
sys.exit(1)
if CLEAR_DEST and DEST_DIR.exists():
shutil.rmtree(DEST_DIR)
ensure_dirs(DEST_DIR / "train", DEST_DIR / "val", DEST_DIR / "test")
class_dirs = [p for p in SRC_DIR.iterdir() if p.is_dir()]
if not class_dirs:
print(f"[ERR] 在 {SRC_DIR} 下未找到类别文件夹。请确认路径是否正确(应为 color/ 下的各类别目录)。")
sys.exit(1)
total_train = total_val = total_test = 0
skipped = 0
for cls_dir in sorted(class_dirs):
imgs = list_images(cls_dir)
if len(imgs) == 0:
print(f"[WARN] 类别 {cls_dir.name} 无图片,跳过。")
skipped += 1
continue
tr_idx, va_idx, te_idx = split_indices(len(imgs))
tr_imgs = [imgs[i] for i in tr_idx]
va_imgs = [imgs[i] for i in va_idx]
te_imgs = [imgs[i] for i in te_idx]
copy_many(tr_imgs, DEST_DIR / "train" / cls_dir.name)
copy_many(va_imgs, DEST_DIR / "val" / cls_dir.name)
copy_many(te_imgs, DEST_DIR / "test" / cls_dir.name)
total_train += len(tr_imgs)
total_val += len(va_imgs)
total_test += len(te_imgs)
print(f"[OK] {cls_dir.name}: {len(imgs)} => train {len(tr_imgs)}, val {len(va_imgs)}, test {len(te_imgs)}")
print("\n====== 汇总 ======")
print(f"类别总数:{len(class_dirs)}(跳过空类 {skipped})")
print(f"Train: {total_train} | Val: {total_val} | Test: {total_test}")
print(f"输出目录:{DEST_DIR.resolve()}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
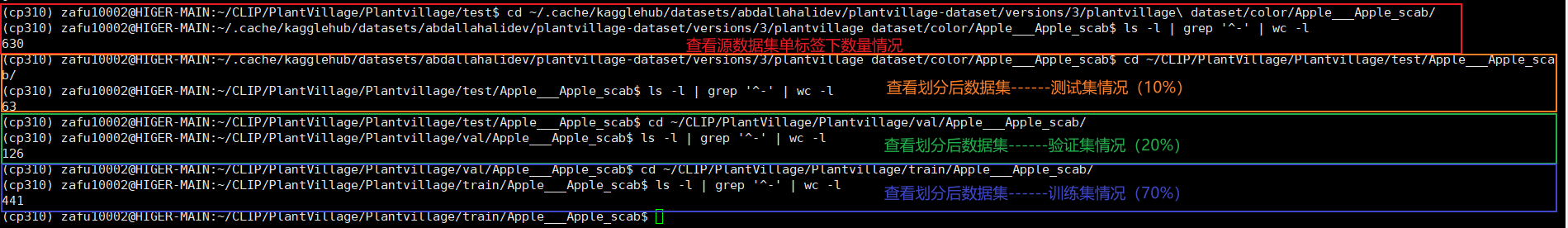
main()现在当前工作目录下应当会看到 ./PlantVillage文件夹,有三个子文件夹:test,train和val,使用命令ls -l | grep '^-' | wc - 可以检查文件夹内文件数量情况,确保测试集:验证集:训练集为1:2:7。
2.3 对划分后的数据集进行规范化处理preprocess.py
import os
from pathlib import Path
from PIL import Image
from tqdm import tqdm
# 1. 定义你的原始数据集路径
source_dir = Path("./Plantvillage")
# 2. 定义你想要保存新数据集的路径
target_dir = Path("./Plantvillage_224")
# 3. 定义我们想要的统一尺寸
new_size = (224, 224)
# 确保 PIL 使用高质量的缩放算法
resample_filter = Image.Resampling.BILINEAR
def preprocess_images():
# 遍历 train, val, test 文件夹
for split in ["train", "val", "test"]:
split_path = source_dir / split
target_split_path = target_dir / split
if not split_path.is_dir():
print(f"Skipping {split_path}, not a directory.")
continue
# 获取所有类别文件夹 (e.g., "Tomato___Bacterial_spot")
class_dirs = [d for d in split_path.iterdir() if d.is_dir()]
print(f"Found {len(class_dirs)} classes in {split}...")
# 使用 tqdm 显示总进度
for class_dir in tqdm(class_dirs, desc=f"Processing {split} set"):
# 在新目录中创建对应的类别文件夹
target_class_path = target_split_path / class_dir.name
target_class_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# 遍历这个类别中的所有图片
# (假设是 .jpg, .JPG, .jpeg, .png)
image_files = list(class_dir.glob("*.jpg")) + \
list(class_dir.glob("*.JPG")) + \
list(class_dir.glob("*.jpeg")) + \
list(class_dir.glob("*.png"))
for image_path in image_files:
try:
with Image.open(image_path) as img:
# 1. 转换为 "RGB" (防止有些是 P 模式或 RGBA)
# 2. 缩放
# 3. 保存
img_rgb = img.convert("RGB")
img_resized = img_rgb.resize(new_size, resample_filter)
#base_name = image_path.stem
# 定义新图片的保存路径
new_image_path = target_class_path / image_path.name
img_resized.save(new_image_path, "JPEG",quality=95)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {image_path}: {e}")
print("--- Pre-processing Complete!(V2) ---")
print(f"All images resized and saved to {target_dir}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
preprocess_images()2.4 创建数据加载文件data_loader.py
import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from pathlib import Path
NW = 32
CLIP_MEAN = [0.48145466, 0.4578275, 0.40821073]
CLIP_STD = [0.26862954, 0.26130258, 0.27577711]
def load_data(data_dir, batch_size=384):
"""
加载训练、验证和测试数据
"""
data_dir = Path(data_dir)
# 数据增强和预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
#transforms.Resize((224, 224)), # 调整大小
transforms.ToTensor(), # 转换为 Tensor
transforms.Normalize(mean=CLIP_MEAN,std=CLIP_STD) # 标准化
])
# 使用 ImageFolder 加载数据集
train_data = datasets.ImageFolder(root=data_dir / 'train', transform=transform)
val_data = datasets.ImageFolder(root=data_dir / 'val', transform=transform)
test_data = datasets.ImageFolder(root=data_dir / 'test', transform=transform)
# 创建 DataLoader
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,num_workers=NW,pin_memory=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_data, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,num_workers=NW,pin_memory=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,num_workers=NW,pin_memory=True)
return train_loader, val_loader, test_loader
# 检查加载的数据集
if __name__ == "__main__":
data_dir = "./Plantvillage_224" # 你的数据集路径
train_loader, val_loader, test_loader = load_data(data_dir)
# 打印一些batch数据检查加载是否正确
data_iter = iter(train_loader)
images, labels = next(data_iter)
print(f"Batch of images shape: {images.shape}")
print(f"Batch of labels shape: {labels.shape}")
2.5 创建模型model.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class PlantDiseaseModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels_img=512, out_channels_img=256, num_classes=38):
"""
一个标准的图像分类模型,它接收来自 CLIP 的 512 维特征。
"""
super(PlantDiseaseModel, self).__init__()
# 1. 图像特征处理层
# 输入 512 (来自 CLIP), 输出 256
self.image_fc = nn.Linear(in_channels_img, out_channels_img)
# 2. 最终分类层
# 输入 256 (来自 image_fc), 输出 num_classes
self.fc = nn.Linear(out_channels_img, num_classes)
# 3. [删除] 不再需要 text_fc
# self.text_fc = ...
# 4. [删除] 不再需要在这里加载 CLIP
# self.model, self.transform = ...
def forward(self, image_features):
"""
定义模型的前向传播。
输入 'image_features' 是 CLIP 已经提取好的 [batch_size, 512] 特征。
"""
# 1. 通过图像层
# [B, 512] -> [B, 256]
x = torch.relu(self.image_fc(image_features.view(image_features.size(0), -1)))
# 2. 通过最终分类层
# [B, 256] -> [B, num_classes]
output = self.fc(x)
return output2.6 创建训练文件train.py
#train
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix,classification_report
from tqdm import tqdm
from model import PlantDiseaseModel # 导入 *修改后* 的模型
from data_loader import load_data
import clip
# 选择设备
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print(device)
# 加载数据集
data_dir = "./Plantvillage_224"
train_loader, val_loader, test_loader = load_data(data_dir)
# --- [修改] ---
# (PlantVillage 是 38 类)
num_classes = 38
model = PlantDiseaseModel(in_channels_img=512, out_channels_img=256, num_classes=num_classes).to(device)
# --- [修改结束] ---
# 强制模型为 float32
model = model.float()
# 设置损失函数和优化器
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
# 加载 CLIP 模型 (这部分保留,用于在 *训练脚本* 中提取特征)
clip_model, preprocess = clip.load("ViT-B/32", device=device)
# 训练函数
def train(model, train_loader, val_loader, num_epochs=10):
best_accuracy = 0.0 # 跟踪最佳准确率
best_model_path = "best_model.pth" # 定义模型保存路径
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model.train() # 设置为训练模式
running_loss = 0.0
# 使用 tqdm 包装 train_loader
for images, labels in tqdm(train_loader, desc=f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{num_epochs} Training"):
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
images = images.float()
labels = labels.long()
# 1. 获取图像特征 (来自 CLIP)
# (在 no_grad() 中运行 clip_model 以节省显存和时间)
with torch.no_grad():
image_features = clip_model.encode_image(images)
image_features = image_features.float()
# 2. 获取模型输出 (前向传播)
outputs = model(image_features)
# 3. 计算损失 (在这里定义 'loss')
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# --- [这是你遗漏的部分 END] ---
# 反向传播并更新权重
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清零梯度
loss.backward() # 计算梯度 (现在 'loss' 已被定义)
optimizer.step() # 更新权重
running_loss += loss.item() # 累加损失
print(f"\nEpoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {running_loss/len(train_loader)}")
# 每个 epoch 后进行验证
val_accuracy = validate(model, val_loader)
# 检查这是否是迄今为止最好的模型
if val_accuracy > best_accuracy:
best_accuracy = val_accuracy
# 保存当前模型的权重
torch.save(model.state_dict(), best_model_path)
print(f"*** 新的最佳模型已保存,准确率: {best_accuracy * 100:.2f}% ***")
# 验证函数
def validate(model, val_loader):
model.eval()
all_preds = []
all_labels = []
# 使用 tqdm 包装 val_loader
with torch.no_grad():
for images, labels in tqdm(val_loader, desc="Validating"):
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
images = images.float()
labels = labels.long()
# 1. 获取图像特征
image_features = clip_model.encode_image(images)
image_features = image_features.float()
# 2. 获取模型输出
outputs = model(image_features)
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
all_preds.extend(preds.cpu().numpy())
all_labels.extend(labels.cpu().numpy())
# 计算准确率
accuracy = accuracy_score(all_labels, all_preds)
cm = confusion_matrix(all_labels, all_preds)
print(f"Validation Accuracy: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%")
print("混淆矩阵 (Validation):")
print(cm)
return accuracy # <-- [修改] 返回计算出的准确率
# 测试函数
def test(model, test_loader):
print("\n--- 启动测试阶段 ---")
model.eval() # 设置模型为评估模式
all_preds = []
all_labels = []
# 从 test_loader 中获取类别名称,用于报告
try:
class_names = test_loader.dataset.classes
except:
class_names = [str(i) for i in range(num_classes)] # 备用方案
with torch.no_grad():
# 使用 tqdm 显示进度条
for images, labels in tqdm(test_loader, desc="Testing"):
images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device)
images = images.float()
labels = labels.long()
# 1. 获取图像特征 (clip_model 是全局变量)
image_features = clip_model.encode_image(images)
image_features = image_features.float()
# 2. 获取模型输出
outputs = model(image_features)
# 3. 获取预测
_, preds = torch.max(outputs, 1)
all_preds.extend(preds.cpu().numpy())
all_labels.extend(labels.cpu().numpy())
# 计算指标
accuracy = accuracy_score(all_labels, all_preds)
cm = confusion_matrix(all_labels, all_preds)
print(f"\n--- 测试结果 ---")
print(f"Test Accuracy: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%")
print("\n混淆矩阵 (Test):")
print(cm)
# 打印分类报告 (包含精确率, 召回率, F1-score)
print("\n分类报告 (Test):")
print(classification_report(all_labels, all_preds, target_names=class_names, digits=4))
# 开始训练
if __name__ == "__main__":
best_model_path = "best_model.pth"
# 1. 训练模型 (现在它会自动保存 'best_model.pth')
train(model, train_loader, val_loader, num_epochs=20)
print("\n--- 训练完成 ---")
print("正在加载最佳模型权重用于测试...")
# 2. 加载保存的 *最佳* 模型权重
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(best_model_path))
# 3. 使用加载的 *最佳* 模型进行测试
test(model, test_loader)3.使用教程
0.文件目录结构:
(工作)根目录
-dataset
--color
-data_loader.py
-split_data.py
-model.py
-train.py
1.先运行pip install -r requirements.txt 安装依赖
2.运行split_data.py划分数据集
3.运行train.py训练
4.训练结果
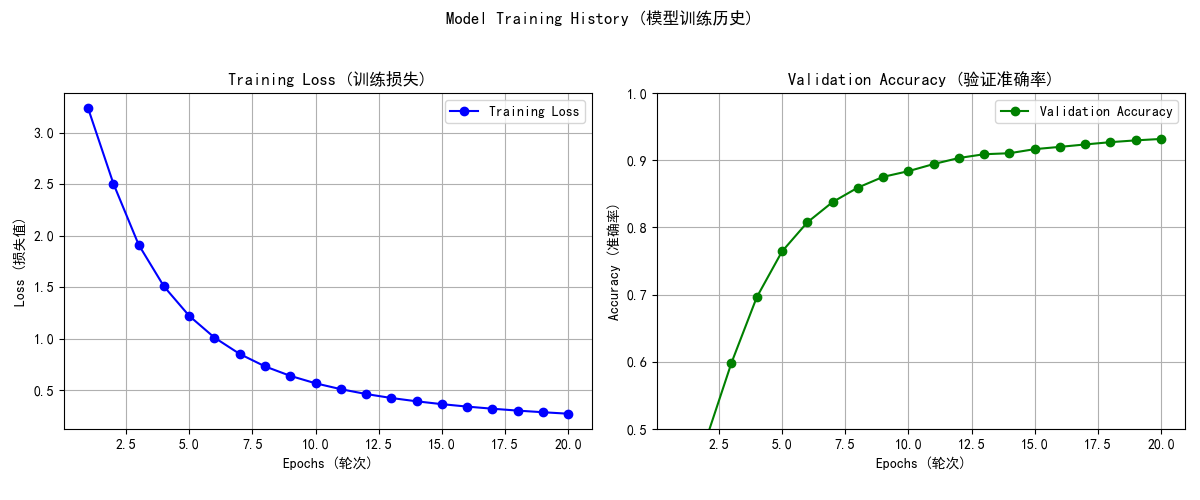
在Epoch为20时,有最高准确率为93.18%
模型在测试集上实现了93.49%的准确率。
precision recall f1-score support
accuracy 0.9349 5435
macro avg 0.9030 0.8849 0.8910 5435
weighted avg 0.9322 0.9349 0.9320 5435
训练损失和验证准确率与Epoch关系如下:
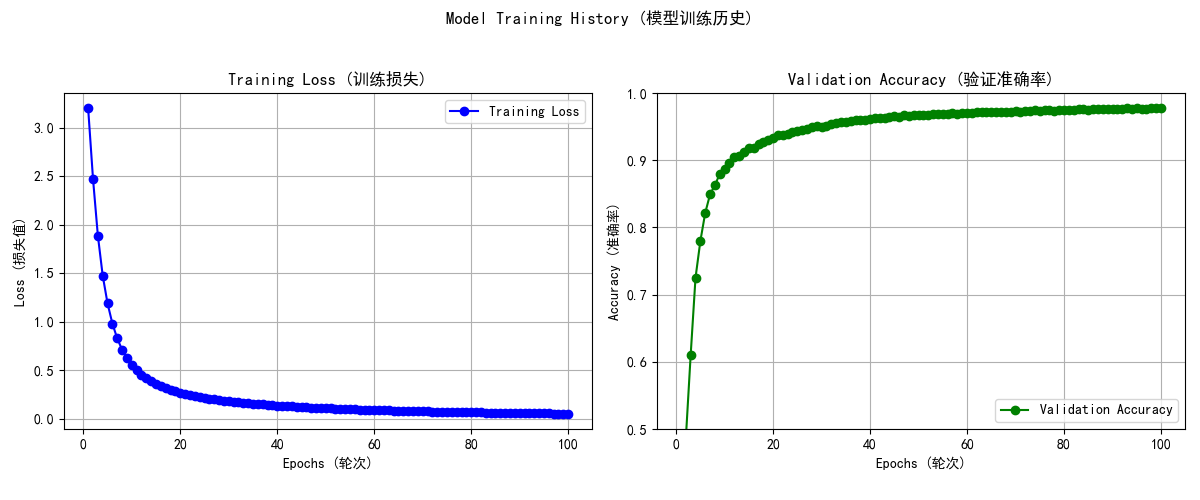
在Epoch为100时,有最高准确率97.84%
模型在测试集上实现了97.88%的准确率。
具体训练结果可以看这里:
微信扫描下方的二维码阅读本文

